How Leaders Can Adapt Styles To Elevate Performance Based on DISC Profiles Through Tuckman's 4 Phases of Group Development.
Have you ever felt mis-managed? In leading people with diverse personalities, leaders who understand that each responds differently in times of change and adapts will boost team performance. On the otherhand, leaders who lead with the same style will inevitably (and unknowingly) mis-manage some team members and undermine team performance. In many cases, remote work has added to the challenge of understanding team members. This directly impacts challenges of turnover, workplace stress, poor productivity, and absenteeism, etc.
Leadership Styles
The effectiveness of leadership within a team can be enhanced by understanding and adapting to various personality styles and leading through the Dr. Tuckman's 4 stages of team development. Leaders can modify their leadership techniques based on DISC personality profiles in alignment with Bruce Tuckman's 4 Stages of Group Development. Regardless of team stage, the leaders who acquire and apply behavioural understanding with team members will increase engagement, reduce turnover and enhance performance results.
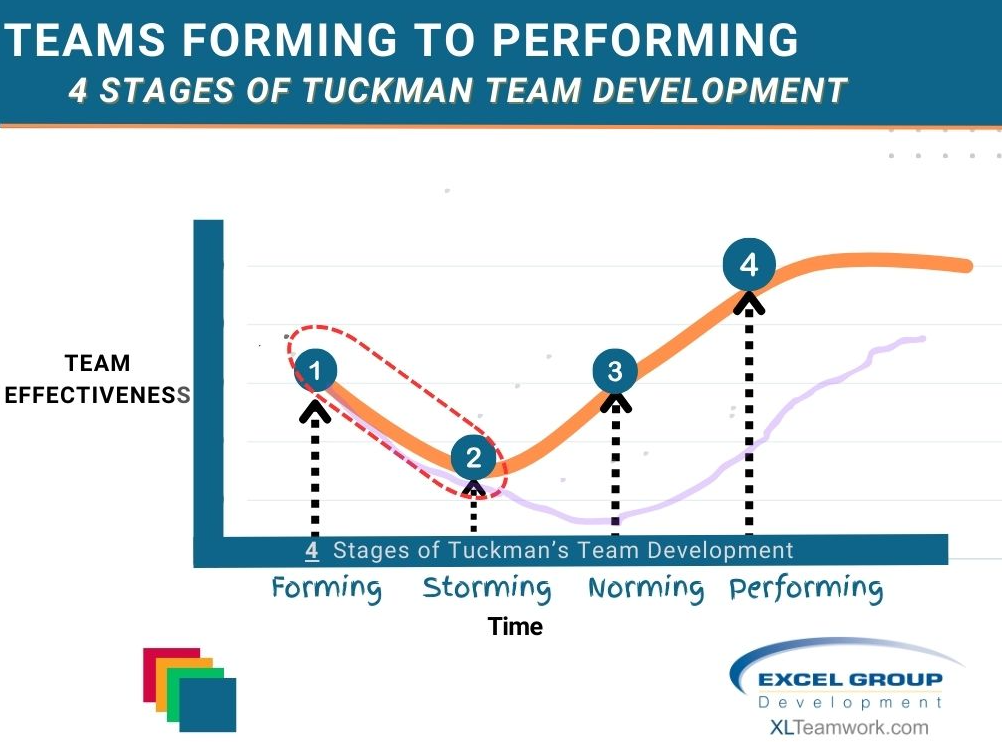
Utilizing DISC Profiles in Tuckman's Stages of Group Development
The DISC model categorizes behavior into four primary styles: Dominance (D), Influence (I), Steadiness (S), and Conscientiousness (C), each influencing how individuals react under varying circumstances. Tuckman’s model, on the other hand, outlines four crucial stages of team development: (1)-Forming, (2)-Storming, (3) Norming, and (4)Performing. By merging insights from both models, leaders can foster stronger, more cohesive teams.
- Forming Stage
During the Forming stage, team members are generally polite and enthusiastic, exploring the boundaries of the project and their responsibilities. Here, understanding the DISC profiles can help leaders tailor their approach to meet the instinctual needs of the team members.
Dominance (D): Individuals with a D profile are driven and ambitious. Leaders should set clear goals and provide these members with challenges and autonomy to harness their strengths.
Influence (I): Those with an I profile thrive on interactions and are often quite persuasive and charming. During this stage, make use of their natural enthusiasm to foster a positive team spirit and encourage open communication.
Steadiness (S): S types value stability and are cooperative. Leaders should assure them by outlining clear processes and expected behaviors, thus providing a sense of security and belonging.
Conscientiousness (C): C types are detail-oriented and cautious. Ensure there are precise standards and schedules to follow, which align with their need for structure and efficiency.
- Storming Stage
 As the team progresses to the Storming stage, conflicts and challenges frequently arise. This stage requires astute leadership to manage the dynamics and harness the strengths of different DISC profiles.
As the team progresses to the Storming stage, conflicts and challenges frequently arise. This stage requires astute leadership to manage the dynamics and harness the strengths of different DISC profiles.Dominance (D): D types may try to assert control as tensions build. Leaders should channel their assertiveness into productive debate and decision-making roles that tap into their problem-solving abilities.
Influence (I): I types can help mediate conflicts by using their interpersonal skills to enhance communication and morale. Leaders should encourage them to take on roles that utilize these strengths.
Steadiness (S): In storming, S types might feel overwhelmed by conflict. Leaders can help by fostering a supportive environment and ensuring their voices are heard, maintaining a sense of team harmony. The challenge is they may not fully express their feelings to a leader.
Conscientiousness (C): C types can become cynical about rushed decisions. Leaders need to involve them in analyzing proposals and creating detailed plans to address their need for systematic approaches.
Effective Leaders Navigate the Storm
Leaders who fail to handle the "Forming" and "Storming" phases effectively, risk a longer period of "Storming" resulting in higher turnover costs, and poor productivity. Those who focus on leading well through the first three stages will achieve superior perforamnce/results in their team execution.
(To Learn more about Disc - see Blog Post " Understanding Disc " )
- Norming Stage
In the Norming stage, the team starts to find its rhythm and learn how to work together effectively. Here, leadership should focus on strengthening relationships and solidifying structures and processes.
 Dominance (D): D types should be encouraged to take the lead on tasks that require strong decision-making and risk management to foster a sense of achievement and to capitalize on their drive.
Dominance (D): D types should be encouraged to take the lead on tasks that require strong decision-making and risk management to foster a sense of achievement and to capitalize on their drive.Influence (I): Leaders should continue to leverage the I type's natural ability to motivate and inspire others, encouraging their role in team-building activities.
Steadiness (S): By this stage, S types contribute significantly to the team's consistency and reliability. The leadership should appreciate their loyalty and dependability, ensuring they feel valued and integral to the team’s success.
Conscientiousness (C): Leaders should allocate detailed-oriented tasks to C types, ensuring accuracy and compliance. Their methodical approach will be essential in maintaining the established systems and processes.
Performing Stage
The Performing stage is where high levels of productivity and performance are observed. Effective leadership is crucial to maintain momentum and optimize productivity based on DISC profile attributes.
Dominance (D): Empower D types by setting challenging targets and giving them the liberty to innovate. This feeds their need for achieving results and leading from the front.
Influence (I): Encourage I types to share their successes and learning experiences. This can inspire continuous improvement and positive engagement across the team.
Steadiness (S): S types should be encouraged to maintain the group's operational stability. Their consistency is crucial in this high-performing stage to ensure sustained success.
Conscientiousness (C): Keep C types engaged with roles that require precision and adherence to high standards, which are crucial during this stage of optimized team functioning.
Conclusion
Effectively managing a team through the stages of development requires a nuanced understanding of both the team’s current dynamics and the individual DISC profiles of its members. By tailoring leadership approaches to align with both Tuckman's stages and the distinct characteristics of the DISC model, leaders can significantly enhance team cohesion, productivity, and overall success.
Follow XLTeamwork on Linked In
(Learn more about DISC behavioural styles here.)
